The AIS transponder class A is a very effective tool for tracking and monitoring ships. It is able to transmit data about the ship’s position, speed, and heading. This information can be used by other ships or by land-based authorities to track the ship’s progress and help ensure its safety.
An Automatic Identification System (AIS) transponder, also known as a transceiver, is a location and vessel information reporting system that makes use of Very High Frequency (VHF) digital transmissions. It is installed on boats and vessels to regularly share their location, position, course, and speed with other similarly equipped vessels. The data can also be used to avoid collisions and track other vessels.
How does an AIS transponder work?
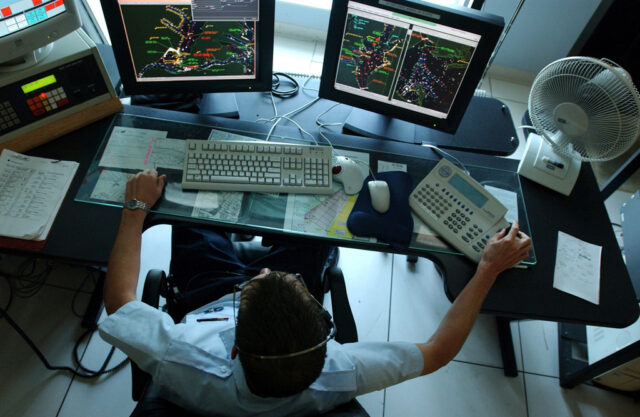

Class A AIS transponder is a device that is used to transmit information about a vessel’s position, speed, and heading. This information is then received by other vessels or shore stations that are equipped with AIS receivers. The main purpose of an AIS transponder is to improve safety at sea by allowing vessels to be aware of the location and movements of other nearby vessels.
AIS transponders are required on all commercial vessels over 300 gross tons, and on all passenger ships regardless of size. Most large recreational boats also now carry AIS transponders.
An AIS transponder transmits information in two ways: via an integrated VHF radio transmitter, and via an integrated GPS receiver. The VHF transmitter broadcasts information about the vessel’s position, speed, and heading at regular intervals. This information can be received by any other vessel or shore station within the range that is equipped with an AIS receiver. The GPS receiver constantly calculates the vessel’s position based on satellite signals, and this information is also transmitted periodically via the VHF transmitter. In addition to the regular broadcasts, an AIS transponder will also transmit a “safety message” if it detects a collision risk.
Type of Transponder
Class A AIS transponders – transmit at a higher VHF signal power and more frequently, allowing them to be received by more distant vessels. They are usually installed on large vessels, such as cargo ships and large passenger vessels due to regulatory requirements.
Class B transponders – transmit at a lower power and at a lower reporting rate than class A transponders. They are also typically lower in cost.
What are the benefits of using an AIS transponder?
An AIS transponder is a powerful tool that can help boaters stay safe on the water.
Here are four benefits of using an AIS transponder:
- Increased Visibility: An AIS transponder broadcasts your boat’s position, course, and speed to other boats in the area. This information can be used by nearby vessels to avoid collisions.
- Enhanced Safety: In an emergency, an AIS transponder can be used to send out a distress signal that will alert nearby boats and the Coast Guard of your location.
- Better Communication: An AIS transponder allows you to communicate with other vessels equipped with AIS technology, even if they are out of sight or beyond radio range. This is especially useful for coordinating group activities like fishing or racing.
- Improved Navigation: Many modern chart plotters have the ability to display information from nearby AIS-equipped boats. This can help you avoid crowded areas or dangerous waters.




