What are Equities: Definition, Types, Investment in Equity
What are Equities?
The balance sheet contains equity, which is one of the most commonly utilized data by analysts to assess a company’s financial health. The amount of money that would be given to a company’s shareholders if all of the company’s assets were liquidated and all of the debt was paid off in the event of liquidation is known as equity, also known as shareholders’ equity.
Shareholder equity can also be used to represent a company’s book worth, and equity can be utilized to make a payment-in-kind arrangement. It also shows how much of a company’s stock is owned pro-rata. In the case of an acquisition, it is the number of a company’s revenues less any debts owed by the company that was not transferred with the transaction.
Read Top 10 factors before buying a stock.
Shareholder equity can also be used to represent a company’s book worth. Equity can be utilized to make a payment-in-kind arrangement. It also shows how much of a company’s stock is owned pro-rata.
The balance sheet contains equity, which is one of the most commonly utilized data by analysts to assess a company’s financial health.
Shareholders Equity – How Does it Function?
The capital raised by a firm is known as equity, and it is used to buy assets, invest in initiatives, and fund operations. The “assets-minus-liabilities” shareholder equity equation offers a clear picture of a business’s finances, readily comprehended by investors and analysts, by comparing real numbers indicating everything the company owns and everything it owes.
A company can raise capital by issuing debt or equity, and investors prefer equity investments because they allow them to participate more fully in their earnings and growth.
Shareholders who own stock will vote on business decisions and board of director elections. The value of a company’s investors might be positive or negative. If the answer is yes, its assets are sufficient to satisfy its liabilities. If the balance sheet is negative, the company’s obligations exceed its assets, known as balance sheet insolvency.
These equity ownership benefits encourage shareholders to remain invested in the business. The value of an investor’s investment in a firm is reflected by the proportion of its shares, which is why equity is significant. Shareholders who own stock in a corporation can benefit from capital gains and dividends.
Investors frequently see negative shareholder equity as a hazardous or lousy investment. On its own, shareholder equity is not a reliable predictor of a company’s financial health; nevertheless, when combined with other tools and indicators, an investor may correctly assess its health.
How To Calculate Shareholders Equity?
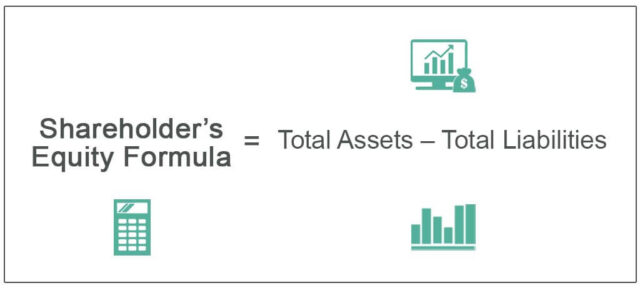
To calculate a company’s equity, apply the formula and computation below, derived using this equation:
Shareholders’ Equity= Total Assets−Total Liabilities
This information may be obtained on the balance sheet, which should be completed in the following four steps:
- Find the firm’s total assets on the balance sheet for the time period.
- Find total liabilities, which should be recorded on the balance sheet separately.
- To calculate shareholder equity, subtract total liabilities from total assets.
- It’s important to remember that real assets equal liabilities and total equity.
Shareholder equity is calculated by subtracting the value of treasury shares from a company’s share capital and retained earnings. This strategy, on the other hand, is less popular. Though both techniques provide the same amount, total assets and liabilities give a more accurate picture of a company’s financial health.
Elements Of Shareholders Equity
The amount of cumulative retained earnings might eventually surpass the equity capital given by investors. Consider retained earnings to be savings since they reflect a sum of profits that have been preserved, set aside, or kept for future use. As the corporation reinvests a portion of its earnings, retained earnings expand.
Companies acquire treasury shares, and their value is recorded in a separate account called treasury stock, which is maintained distinct from the investor capital and retained earnings accounts. Treasury shares or stock are equity that the firm has acquired from current shareholders.
When management cannot use all of the available equity capital in the most profitable ways, a buyback may be implemented. When a business needs money, it may reissue treasury shares to investors. Many people think of stockholders’ equity as a corporation’s net assets, or the amount shareholders would get if the firm liquidated its assets and paid off all of its obligations.
For organizations that have been in business for a long time, retained earnings are frequently the most significant component of stockholders’ equity. The percentage of net earnings that were not given to shareholders as dividends is known as retained earnings, and it is a component of shareholder equity.
What is the difference between stocks and equities?
The Basic and most important difference between Stocks and Equities is The Equities can’t be buy and sell by General Public as Equities are not traded on Stock Exchange, Whereas the Stocks are traded on Stock exchanges so that Stock of that Company can be Buy and Sell by General Public.
By investing Money in a company you get share of that company.
Application of Equity for Investors
If, for example, the firm has typically traded at a price to book value of 1.5, an investor would be hesitant to pay more than that until the company’s prospects have fundamentally changed. For investors, equity is a crucial notion. For example, while evaluating a firm, an investor can use shareholders’ equity as a criterion to determine if a specific acquisition price is too high. On the other hand, an investor may feel safe purchasing shares in a somewhat poor company if the price paid is sufficiently low about the company’s equity.

Different Forms Of Equity
Beyond analyzing enterprises, the notion of equity has many uses. We might conceive equity in a broader sense as the amount of ownership in an asset after all obligations have been paid off.
Listed below are a few popular equity variations:
- A stock or other security that represents a company’s ownership stake.
- The value of securities in a margin account minus the amount borrowed from the brokerage in margin trading.
- The sum of the capital given by the owners or shareholders plus the retained earnings on a company’s balance sheet (or losses). This is also known as stockholders’ or shareholders’ equity.
- The difference between the property’s current fair market value and the amount owed on the mortgage by the owner. It is the sum received by the owner after selling a property and paying off any debts.
- When a company goes bankrupt and needs to liquidate, equity refers to the money left over after paying creditors.
Want to know about NFTs and buy and sell NFTs read the complete guide here.
Private Equity
The term “private equity” refers to examining a company that is not publicly listed. The accounting equation still holds, with declared equity on the balance sheet being the amount left over after removing liabilities from assets to arrive at a book value estimate.
When an investment is publicly traded, the market value of equity may be readily determined by looking at the firm’s stock price and market capitalization. Because the market process does not exist for private entities, different methods of estimating value must be used.
Privately held businesses can then raise funds by selling shares in private placements. Pension funds, university endowments, insurance firms, and accredited individuals are examples of private equity investors.
Private equity can be used at various stages of a company’s life cycle. A fledgling firm with no sales or revenues can usually not afford to borrow, and thus it must rely on friends and family or individual “angel investors” for funding.
The loan is generally secured by the cash flow or assets of the firm being bought. A private loan issued by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital company is called mezzanine debt. Private equity is frequently offered to funds and investors who specialize in direct private equity investments or public company leveraged buyouts.
A corporation accepts a loan from a private equity firm to support the acquisition of a division of another company in an LBO deal.. In a subordinated loan or warrants, common stock, or preferred stock, mezzanine deals frequently combine debt and equity.

Private Equity Financing – Different Types
Private investment in a public company is the last sort of private equity. A PIPE is the acquisition of shares in a corporation by a private investment firm, a mutual fund, or other eligible investors at a discount to the current market value per share to raise cash. Venture capitalists provide most private equity funding for an early minority share.
Venture investors want to make a significant profit right away and exit their investments in five to seven years. A venture capitalist may take a seat on the board of directors of one of its portfolio firms to play a more active role in the company’s direction. Private equity, unlike shareholder equity, is not available to the average person. Private equity and venture capital partnerships are only open to “accredited” investors with a net worth of at least $1 million.
Home Equity
The amount of equity in a home is calculated by subtracting the mortgage debt outstanding from the total value of the property. Home equity is frequently a person’s most valuable asset, and it can be used to get a home equity loan, also known as a second mortgage or a home equity line of credit.
Home equity is essentially equivalent to the value of owning a home. Payments paid towards a mortgage, including down payment and growth in property value, result in inequity on a property or house. Taking money out of a property or borrowing against it is an equity takeout.
Brand Equity
A company’s brand can generate intrinsic value over time due to years of promotion and the growth of a client base; This is referred to as “brand equity. It’s vital to remember that when calculating an asset’s equity, especially for more prominent organizations, these assets might comprise tangible and intangible assets, such as the company’s reputation and brand identification.
Negative brand equity is uncommon, although it can happen due to negative news, such as a product recall or a natural disaster. Negative brand equity exists when customers are willing to pay more for a generic or store-brand good than they would for a specific brand name. It refers to the value of a brand compared to a generic or store-brand version of a product.
Comparison – Equity vs Return on Equity
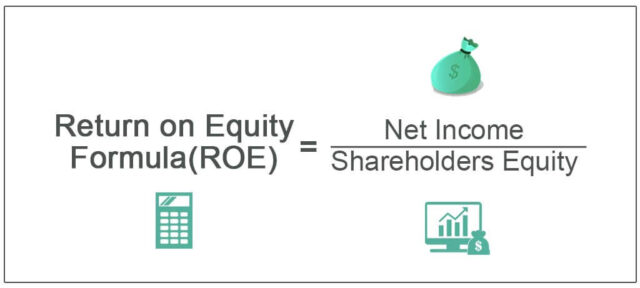
Equity may have a variety of meanings, but it most commonly refers to ownership of an item or a firm, such as investors holding equity in a company. The return on equity is a financial performance metric determined by dividing net income by shareholder equity. Because shareholder equity equals a company’s assets less its debt, ROE is also known as return on net assets.
The return on equity measures how efficiently a company’s assets are used to generate profits. The return on equity (ROE) is a financial term that quantifies how much profit a firm generates from its shareholders’ equity.
Conclusion
So that is all that is required to understand equity. Let us know in the comments if you have any doubts or queries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What are examples of equities?
Ans: The most common Examples of Equities are:
- Common stock.
- Preferred stock.
- Additional paid-in capital.
- Treasury stock.
- Accumulated other comprehensive income / loss.
- Retained earnings.
2. What is the difference between stocks and equities?
Ans: The Basic difference between stocks and equities is that Equities can’t be trade on Stock Exchange as this don’t include participation of General Public, Whereas the Stocks have General Public participation and traded on Stock Exchange.
3. What are Equities?
Ans: The amount of money that would be given to a company’s shareholders if all of the company’s assets were liquidated and all of the debt was paid off in the event of liquidation is known as equity, also known as shareholders’ equity.
4. What does it mean to invest in equities?
Ans: Invest in Equities means Investing your Money in Company by purchasing It’s Share of that Company in Stock Market which is traded on Stock Exchange.




