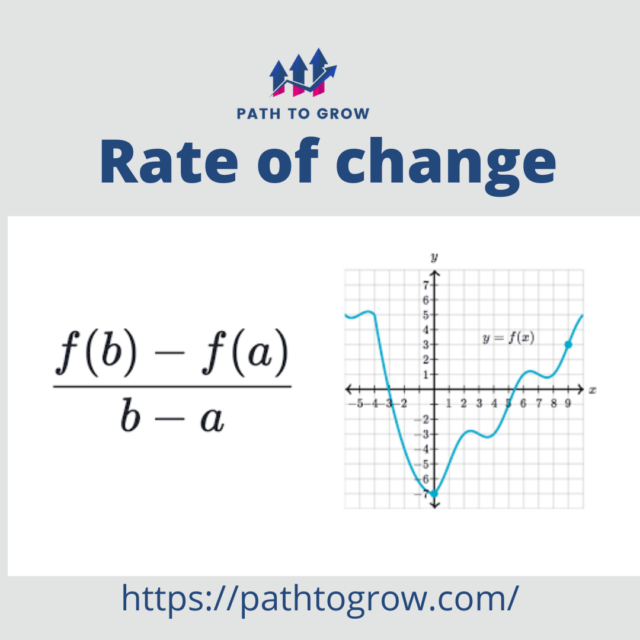
What is Monetary Conditions Index (MCI) – Calculation and Applications
The term monetary conditions index is defined to determine the relative ease of tightness of financial conditions of a country. It is being calculated by using the short-term interest and the rate of exchange of the national currency of a nation. The central government is using this calculation to create or draft monetary policy, and it has become a benchmark now used by approximately all the countries across the world. This article will discuss its definition, calculation, and applications in detail.
learn about max pain options here, it helps your investment and trading better.
Things to Remember
- The monetary conditions index is used to determine the relative ease and tightness of the economic condition by using the exchange rate and short-term interest.
- The Central banks use the monetary conditions index to draft the economic policy.
- The bank of Canada used the MCI index for the first time to find the relation between Canada’s exchange rate and its economy.
- The way to calculate the MCI index may vary from country to country. Still, the objective remains the same to determine the relationship between the exchange rate and a nation’s economy.
Read the top 8 ways which helps you how to be a millionaire, Read here.
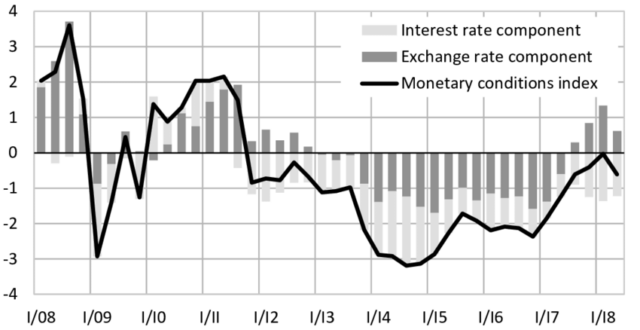
What is Monetary Conditions Index?
First, the Canadian government developed every monetary condition index in 1996 to evaluate the relationship between the interest rates in Canada, the relative trading exchange rate of Canadian currency, and Canada’s economy as a whole. This data is then provided every month for both MCI and its components.
To calculate the Monetary Conditions index, a specific period is chosen by the country’s central banks. Then, they create a chart of the weighted average of interest rate changes and exchange rate changes by comparing it with the actual value of these variables.
You can earn money by sitting at home and doing work online, Read the guide of freelance work online to earn more money online.
In general, this calculation is being used by the central government to determine the effect of short-term monetary policy by finding the changes in the interest rate and the exchange rate set up by the central government by the influence of the foreign exchange market.
Calculations of Monetary Conditions Index
Although every other country has its way of calculating the MCI, the goal remains the same to evaluate the relationship between the change in the exchange rate and interest rate of a country. But sometimes, they might change their mechanism to calculate the MCI, such as Canada.
If you want to invest and searching for investment platform? Here are the best investment apps in 2024.
From 1987 to 1999, the MCI estimation utilized the 90-day business paper rate adjustment. At that point, added a part of the development in the swapping scale of the Canadian dollar (CAD). The C-6 found the middle value of the monetary standards of six of Canada’s significant exchanging accomplices: the United States, Europe, Japan, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and Sweden. This conversion standard estimates the CAD to the C-6 swapping scale.
In 2018, the MCI computation moved to the ostensible Canadian successful conversion standard (CEER). The Canadian-dollar compelling conversion scale list (CERI) supplanted the C-6 record in 2006 and was resigned in 2018 for a new method. This is a weighted normal of reciprocal trade rates for the CAD against the monetary forms of Canada’s most conspicuous exchanging partners.4
Right now, CEER incorporates 17 currencies.4 The nations incorporate those that record for at minimum 0.5% of
- Canadian non-oil trades (for an aggregate of over 93% of those commodities)
- Canadian non-oil imports (for an aggregate of over 91% of those imports)4
The significant monetary standards of the 17 monetary standards incorporate the U.S., Japan, U.K., Switzerland, Australia, and Sweden.
How does stock market work, Read a comprehensive Guide here.
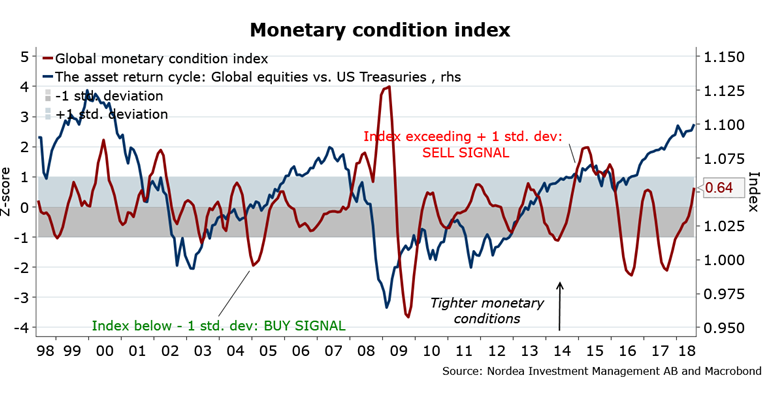
Increase in the Usage of Monetary Condition Index
Right after Canada, Many other countries have also started using the MCI formula to calculate the relationship between the interest rate and the exchange rate. Several central banks are using this to guide the monetary policy for their country. Other than the central banks, other organizations also use this, such as the international monetary fund (IMF) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
The basic to calculate the MCI remains the same as these organizations use the same components; they just apply the different values or weights to the elements in the equations. This technique helps them calculate the exact data, which helps them produce results as accurately as possible. For example, the Directorate-General for Economic and Financial Affairs of the European Commission currently applies 6:1 values on the interest rate and exchange rate for the calculation based on the last received economic results.
However, external components are also used in the calculation in some cases. But central banks mostly prefer to use the fix parameters to calculate the MCI. The effortlessness and straightforwardness of the model might restrict its utilization as the main essential proportion of the viability of the money-related arrangement.
Read about marginal rate of substitution (MRS) Here.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How to Calculate the Monetary Condition index?
Ans: A Monetary Conditions Index (MCI) is a list number determined from a straight Combination of the short-run interest rate and exchange rate.
2. What is a monetary indicator?
Ans: Financial markers identify with the money-related arrangement just like the cash supply. There is a recorded connection between the stock of cash and costs. Like this, it is a decent pointer at the degree of costs in the economy.
3. What are instruments of monetary policy?
Ans: Fundamental instruments of the financial strategy are: Cash Reserve Ratio, Statutory Liquidity Ratio, Bank Rate, Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate, and Open Market Operations.